dipole_radiation Class Reference
A class. More...
#include <dipole_radiation.h>
Public Member Functions | |
| dipole_radiation (dipole_parameters p) | |
| A Constructor. | |
| ~dipole_radiation () | |
| A Destructor. | |
| void | reset_parameters (dipole_parameters p) |
| A method for resetting parameters. | |
| void | set_dipole_field (Array< complex< double >, 3 > E_x, Array< complex< double >, 3 > E_y, Array< complex< double >, 3 > E_z) |
| A method for loading the input dipole field from arrays. | |
| void | set_dipole_field (string file_xcomp, string file_ycomp, string file_zcomp) |
| A method for loading the input dipole field from files. | |
| void | calculate_radiation (Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_rad_x, Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_rad_y, Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_rad_z) |
| A method for calculating far-field radiation on the spherical surface of the collecting lens. | |
| void | calculate_refraction (Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_refr_x, Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_refr_y, Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_refr_z) |
| A method for calculating far-field radiation after refraction at the spherical surface of the collecting lens. | |
| void | calculate_refracted_radiation (Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_rad_x, Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_rad_y, Array< complex< double >, 2 > &E_rad_z) |
| A method for calculating far-field radiation after refraction at the spherical surface of the collecting lens. | |
| void | save_results (string idir) |
| A method for saving the calculated results in a file. | |
Detailed Description
A class.Create an instance of this class, pass the simulation parameters and the source dipole strengths to calculate the far field radiation on the sphereical surface of the collecting lens. A method is also provided to calculate the radiation after the refraction at the collecting lens' spherical surface. This class uses the arrays from the blitz++ library. Hence to use this class and the focus3d class it would be a good idea to read up the documentation of blitz++ arrays.
Using this class in your code is pretty simple. The following piece of code generates the vectorial far field due to a dipole distribution with all the dipoles being oriented along x-direction:
- #include "dipole_radiation.h"
- int main()
- {
- dipole_parameters param("parameters.dat"); // parameters.dat is a valid parameters file (see focus3d_parameters)
- // define two-dimensional matrices to receive the calculated radiation
- Array<complex<double>,2> E_rad_x(param.Ntheta,param.Nphi);
- Array<complex<double>,2> E_rad_y(param.Ntheta,param.Nphi);
- Array<complex<double>,2> E_rad_z(param.Ntheta,param.Nphi);
- dipole_radiation drad(input_params);
- drad.calculate_refracted_radiation(E_rad_x, E_rad_y, E_rad_z);
- drad.save_results("directory_prefix");
- }
- Examples:
Constructor & Destructor Documentation
| dipole_radiation::dipole_radiation | ( | dipole_parameters | p | ) |
A Constructor.
Takes the input parameters through an object of dipole_parameters class which is an alias to focus3d_parameters class and initializes all the internal matrices. It calls internally the dipole_parameters::test() member function to test the sanity of the parameters. If insane, the program quits. Internally, this constructor calls the reset_parameters() method.
- Parameters:
-
p - A focus3d_parameters object
| dipole_radiation::~dipole_radiation | ( | ) |
A Destructor.
Releases the the memory associated with all the allocated internal matrices.
Member Function Documentation
| void dipole_radiation::reset_parameters | ( | dipole_parameters | p | ) |
A method for resetting parameters.
Reloads the new parameters and redefines the sizes of the internal matrices.
- Parameters:
-
p an instance of focus3d_parameters class. Note the effect of using this function is that it resets the effects of previous calls to set_dipole_field.
- Returns:
- void.
| void dipole_radiation::set_dipole_field | ( | Array< complex< double >, 3 > | E_x, | |
| Array< complex< double >, 3 > | E_y, | |||
| Array< complex< double >, 3 > | E_z | |||
| ) |
A method for loading the input dipole field from arrays.
The dipole field is the field that is at the focus of the focusing objective. It has three components corresponding to x, y and z polarizations. If we denote them as E_x, E_y and E_z, then the inputs should be three matrices of the size of (Nx, Ny, Nz), i.e. E_x = E_x(x,y,z), E_z = E_y(x,y,z) and E_z = E_z(x,y,z). The default case is E_x = 1; E_y =0; E_z = 0.
- Parameters:
-
[in] E_x - E_x(x,y,z) [in] E_y - E_y(x,y,z) [in] E_z - E_z(x,y,z)
- Returns:
- void.
- Examples:
- radiation_from_focal_volume.cpp.
| void dipole_radiation::set_dipole_field | ( | string | file_xcomp, | |
| string | file_ycomp, | |||
| string | file_zcomp | |||
| ) |
A method for loading the input dipole field from files.
The dipole field is the field that is at the focus of the focusing objective. It has three components corresponding to x, y and z polarizations. If we denote them as E_x, E_y and E_z, then the inputs should be three matrices of the size of (Nx, Ny, Nz), i.e. E_x = E_x(x,y,z), E_z = E_y(x,y,z) and E_z = E_z(x,y,z). (The default case is E_x = 1; E_y =0; E_z = 0.) If these three components are stored in three different files in blitz array format in column major ordering then, this function can be used to load them.
- Parameters:
-
[in] file_xcomp - name of the file containing x-component of the dipole field [in] file_ycomp - name of the file containing y-component of the dipole field [in] file_zcomp - name of the file containing z-component of the dipole field
- Returns:
- void.
| void dipole_radiation::calculate_radiation | ( | Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_rad_x, | |
| Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_rad_y, | |||
| Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_rad_z | |||
| ) |
A method for calculating far-field radiation on the spherical surface of the collecting lens.
Calculates the far-field distributions for all the three components and saves the results in the variables called by reference. xcomp, ycomp and z_comp are matrices of size (Ntheta,Nphi) allocated before passing to this function by reference.
Note: if the far-field is desired at just one point (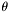 ,
, ) then set the parameter variables Ntheta = Nphi = 1 and theta_min =
) then set the parameter variables Ntheta = Nphi = 1 and theta_min = 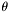 , and phi_min =
, and phi_min =  .
.
- Parameters:
-
[out] E_rad_x - x-component of the far-field [out] E_rad_y - y-component of the far-field [out] E_rad_z - z-component of the far-field
- Returns:
- void.
| void dipole_radiation::calculate_refraction | ( | Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_refr_x, | |
| Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_refr_y, | |||
| Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_refr_z | |||
| ) |
A method for calculating far-field radiation after refraction at the spherical surface of the collecting lens.
Calculates the far-field distributions after refraction for all the three components and saves the results in the variables called by reference. E_refr_x, E_refr_y and E_refr_z are matrices of size (Ntheta,Nphi) allocated before passing to this function by reference.
Note:
- if the far-field is desired at just one point (
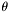 ,
, ) then set the parameter variables Ntheta = Nphi = 1 and theta_min =
) then set the parameter variables Ntheta = Nphi = 1 and theta_min = 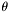 , and phi_min =
, and phi_min =  .
. - call this method only after invoking calculate_radiation(). Internally, this function just performs a coordinate transformation operations on the matrices corresponding to the radiation on the spherical surface of the collecting lens. Hence if this function is called before invoking the calculate_radiation() method, the results would be spurious.
- Parameters:
-
[out] E_refr_x - x-component of the refracted far-field [out] E_refr_y - y-component of the refracted far-field [out] E_refr_z - z-component of the refracted far-field
- Returns:
- void.
| void dipole_radiation::calculate_refracted_radiation | ( | Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_rad_x, | |
| Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_rad_y, | |||
| Array< complex< double >, 2 > & | E_rad_z | |||
| ) |
A method for calculating far-field radiation after refraction at the spherical surface of the collecting lens.
Calculates the far-field distributions after refraction for all the three components and saves the results in the variables called by reference. E_refr_x, E_refr_y and E_refr_z are matrices of size (Ntheta,Nphi) allocated before passing to this function by reference.
Note:
- if the far-field is desired at just one point (
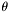 ,
, ) then set the parameter variables Ntheta = Nphi = 1 and theta_min =
) then set the parameter variables Ntheta = Nphi = 1 and theta_min = 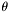 , and phi_min =
, and phi_min =  .
. - Internally, this function invokes calculate_radiation() and calculate_refraction() in series in that order.
- Parameters:
-
[out] E_rad_x - x-component of the refracted far-field [out] E_rad_y - y-component of the refracted far-field [out] E_rad_z - z-component of the refracted far-field
- Returns:
- void.
- Examples:
- radiation_from_focal_volume.cpp.
| void dipole_radiation::save_results | ( | string | idir | ) |
A method for saving the calculated results in a file.
saves the calculated results to different files. The generated output files are:
- x.bar : blitz array corresponding to x coordinates
- y.bar : blitz array corresponding to y coordinates
- z.bar : blitz array corresponding to z coordinates
- theta.bar : blitz array corresponding to
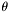 coordinates
coordinates - phi.bar : blitz array corresponding to
 coordinates
coordinates - E_dipole_x.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the x-component of the dipole field
- E_dipole_y.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the y-component of the dipole field
- E_dipole_z.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the z-component of the dipole field
- E_far_x.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the x-component of the far-field
- E_far_y.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the y-component of the far-field
- E_far_z.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the z-component of the far-field
- E_refracted_x.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the x-component of the refracted far-field
- E_refracted_y.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the y-component of the refracted far-field
- E_refracted_z.bar : blitz array cooresponding to the z-component of the refracted far-field
- simulation_parameters.dat : an ascii file with the applied simulation parameters
Note:
- all the files are stored in a subdirectory called (in MATLAB format) [idir '_rad_lam_' + num2str(lambda) + '/']
- the first five files contain one dimensional real data
- the next three files contain three dimensional complex data as a function of (x,y,z)
- the next sixfiles contain two dimensional complex data as a function of (
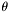 ,
,  )
) - each complex number A+iB is represented as (A,B)
- the class uses the blitz++ arrays in column major format and hence the matrix A(i,j,k) is stored with the index k as the fastest running one and the index i being the slowest running one.
- Parameters:
-
idir - prefix to the directory to which the results have to be saved
- Returns:
- void.
- Examples:
- radiation_from_focal_volume.cpp.
The documentation for this class was generated from the following files:
- dipole_radiation.h
- dipole_radiation.cpp
 1.5.5
1.5.5