Focus3D -- A focal fields package documentation
1.0
- Date:
- June 2006 - May 2008
- Version:
- 1.0
Introduction
This package which consists of a set of c++ header files along with c++ source files is meant to be used for- the calculation of the vectorial fields near the focus of a high numerical aperture objective
- the calculation of coherent far-field radiation from the dipoles present in the focal volume
- the generation of the excitation fields for various coherent microscopy techniques such as coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering (CARS), second-harmonic generation (SHG), third harmonic generation (THG), etc,.
This package provides three classes:
- focus3d_parameters :
- it holds the parameters that are required for simulating the the focal fields and far-field radiation.
- it provides methods for loading, saving and test the integrity of the parameters.
- the objects of this class are used to initialize the rest of the two classes.
- focus3d ::
- provides functions for generating the focal field distribution for arbitrary input fields
- includes methods for integrating scattering effects as perturbations as angular weighting factors
- internally it makes use of the blitz++ arrays for mathematical calculations
- provides functions for saving the results to external files or blitz arrays within the calling program
- dipole_radiation :
- provides functions for calculating the far-field radiation for arbitrary three dimensional dipole distribution
- internally it makes use of the blitz++ arrays for mathematical calculations
- provides functions for saving the results to external files or blitz arrays within the calling program
In a typical program, one can use the focus3d class to generate the focal fields or the excitation fields and pipe this field distribution as the dipole field to the dipole_radiation class to calculate the far-field radiation.
Mathematical background
The focal field distribution (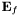 ) at wavelength
) at wavelength  with wavevector magnitude
with wavevector magnitude 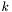 due to a lens of focal length
due to a lens of focal length 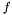 is given in angular spectrum representation as
is given in angular spectrum representation as
![\[ \mathbf{E}_f(x,y,z) = \frac{if}{\lambda}\mathrm{e}^{-ikf} \int_0^{\theta_{max}} \mathrm{d}\theta \int_0^{2\pi}\mathrm{d}\phi \left(\frac{n_1}{n_2}\right)^{1/2} \sqrt{\cos\theta} \sin\theta\, \mathrm{e}^{ik(x\sin\theta\cos\phi + y\sin\theta\sin\phi + z\cos\theta)}\ R^{-1} L^{-1} R \mathbf{E}_{inc} \]](form_6.png)
where the variable 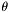 is the polar angle and
is the polar angle and 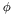 is the azimuthal angle; the limit of integration
is the azimuthal angle; the limit of integration 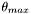 corresponds to the numerical apaerture of the lens;
corresponds to the numerical apaerture of the lens;  is the refractive index before the refraction at the lens and
is the refractive index before the refraction at the lens and  is the refractive index after the refraction at the lens;
is the refractive index after the refraction at the lens;  is the incident field on the lens;
is the incident field on the lens;  and
and  are the coordinate transformation
are the coordinate transformation  matrices are given by
matrices are given by
![\begin{eqnarray*} R(\phi) &=& \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} \cos\phi & \sin\phi & 0\\ -\sin\phi & \cos\phi & 0\\ 0 & 0 & 1\end{array}\right]\\ L(\theta) &=& \left[ \begin{array}{ccc} \cos\theta & 0 & \sin\theta\\ 0 & 1 & 0\\ -\sin\theta & 0 & \cos\theta\end{array}\right] \end{eqnarray*}](form_16.png)
The opeartion  on
on 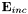 leads to refraction of the incident fields due to the curvature of the lens. If a scattering medium is present between the lens surface and the focal point, the rays that reach the focal point from the lens get perturbed and their amplitudes and phases get scrambled. This scrambling of phase and amplitude by the scattering medium can be modeled as a scalar angular weight function,
leads to refraction of the incident fields due to the curvature of the lens. If a scattering medium is present between the lens surface and the focal point, the rays that reach the focal point from the lens get perturbed and their amplitudes and phases get scrambled. This scrambling of phase and amplitude by the scattering medium can be modeled as a scalar angular weight function,  . These angular weights for various
. These angular weights for various 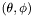 are calculated using Monte-carlo simulations. This weight function can be included in the above formula as
are calculated using Monte-carlo simulations. This weight function can be included in the above formula as
![\[ \mathbf{E}_f(x,y,z) = \frac{if}{\lambda}\mathrm{e}^{-ikf} \int_0^{\theta_{max}} \mathrm{d}\theta \int_0^{2\pi}\mathrm{d}\phi \left(\frac{n_1}{n_2}\right)^{1/2} \sqrt{\cos\theta} \sin\theta\, \mathrm{e}^{ik(x\sin\theta\cos\phi + y\sin\theta\sin\phi + z\cos\theta)}\ G(\theta,\phi) \left(\begin{array}{lllll} {E_i}_x ( C^2_\phi C_\theta + S^2_\phi ) &+& {E_i}_y( -(1-C_\theta) S_\phi C_\phi ) &+& {E_i}_z ( -S_\theta C_\phi )\\ {E_i}_x ( -(1-C_\theta) S_\phi C_\phi ) &+& {E_i}_y( S^2_\phi C_\theta + C^2_\phi ) &+& {E_i}_z ( -S_\theta S_\phi )\\ {E_i}_x ( S_\theta C_\phi ) &+& {E_i}_y( S_\theta S_\phi ) &+& {E_i}_z( C_\theta ) \end{array}\right) \]](form_21.png)
where 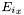 ,
,  , and
, and  are the x- y- and z-components of the incident field and the sine and cosine functions are abbreviated as
are the x- y- and z-components of the incident field and the sine and cosine functions are abbreviated as  and
and  respectively. Evaluation of thie above double integral gives the three components of the electric field at
respectively. Evaluation of thie above double integral gives the three components of the electric field at  near the focus of the lens. In this package, the numerical integration is performed using the Simpson 1/3-rule.
near the focus of the lens. In this package, the numerical integration is performed using the Simpson 1/3-rule.
The above Eq. is used for calculating the focal field for various wavelengths. In the case of CARS, the focal fields for the pump and the Stokes wavelengths are calculated. The CARS excitation at the focal volume is generated by simply multiplying the fields according the relationship
![\[ E_{CARS} = \chi^{(3)} E_{pump}E_{stokes}^{*}E_{pump} \]](form_28.png)
The excitation volume is modeled as a collection of dipoles with their magnitude and orientation being equal to those of the excitation field at that point. Thus the electric vector at a far-field point, say at the surface of the collection lens of focal length f',  is simply a coherent sum of the fields originating from individual points
is simply a coherent sum of the fields originating from individual points  near the focus.
near the focus.
![\[ \mathbf{E}_{far} = -\int\mathrm{d}x\int\mathrm{d}y\int\mathrm{d}z\, \frac{\mathrm{e}^{i\mathbf{k}\cdot\mathbf{R}}}{4\pi\left|\mathbf{R}\right|^3}\ \left[\mathbf{R}(x,y,z) \times \mathbf{R}(x,y,z) \times \mathbf{E}_{dipole}(x,y,z)\right] \]](form_30.png)
where
![\[ \mathbf{R}(x,y,z) = (X-x)\hat{i} + (Y-y) \hat{j} + (Z-z) \hat{k} \]](form_31.png)
with 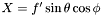 ,
,  , and
, and 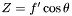 . After performing the vector product operations, we have the far-field electric vector as
. After performing the vector product operations, we have the far-field electric vector as
![\[ \mathbf{E}_{far}(f',\theta,\phi) = -\int\mathrm{d}x\int\mathrm{d}y\int\mathrm{d}z\, \mathrm{e}^{-ik(x\sin\theta\cos\phi + y\sin\theta\sin\phi + z\cos\theta)}\frac{\mathrm{e}^{ikf'}}{4\pi\left|\mathbf{R}\right|^3}\ \left( \begin{array}{lllll} {E_d}_x\left(-(Y-y)^2 - (Z-z)^2\right) &+& {E_d}_y(X-x)(Y-y) &+& {E_d}_z(X-x)(Z-z)\\ {E_d}_x(X-x)(Y-y) &+& {E_d}_y\left(-(X-x)^2 - (Z-z)^2\right) &+& {E_d}_z(Y-y)(Z-z)\\ {E_d}_x(X-x)(Z-z) &+& {E_d}_y(Y-y)(Z-z) &+& {E_d}_z\left(-(X-x)^2 - (Y-y)^2\right)\\ \end{array} \right) \]](form_35.png)
where 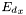 ,
, 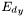 , and
, and 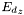 are the x,y, and z-components of the dipole field. This is the field on the spherical surface of the collecting lens. If the collecting lens a complete sphere, then the above Eq. gives the radiation pattern from the dipole distribution. The three dimensional integral in the above equation is numerically calculated in this software package using Simpson 1/3-rule.
are the x,y, and z-components of the dipole field. This is the field on the spherical surface of the collecting lens. If the collecting lens a complete sphere, then the above Eq. gives the radiation pattern from the dipole distribution. The three dimensional integral in the above equation is numerically calculated in this software package using Simpson 1/3-rule.
The field after refraction at the spherical surface is obtained by pre-multiplying 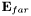 with the coordinate transformation matrix combination
with the coordinate transformation matrix combination  where the matrices
where the matrices  and
and  are defined in the beginning of this section. Hence the refracted field
are defined in the beginning of this section. Hence the refracted field  is
is

The c++ code implemented in this package defines one class, focus3d, to compute  and a second one, dipole_radiation, to compute
and a second one, dipole_radiation, to compute 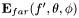 and
and 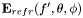 . In this software package, the effects of refractive index mismatch are neglected.
. In this software package, the effects of refractive index mismatch are neglected.
Code organization and important methods
The following paragraphs briefly discuss the usage of this software package in your programs. The pre-requirement to using this package is that the programmer should be familiar with the workings of blitz++ library, especially, the arrays - how they are created, stored and manipulated. The blitz library and its documentation can be obtained from http://www.oonumerics.org/blitz/manual/blitz.html .focus3d_parameters class
Objects of the focus3d_parameters class hold the parameters for simulating the focal fields and the far-field radiation. This class provides methods for setting the default values for the parameters, loading them from a file, saving them to a file, and performing integrity checks on the parameters. All the data members of this class, which are seventeen in number, are all public data types and hence can be changed from the within the code. The important methods of this class are focus3d_parameters::load(), focus3d_parameters::save(), focus3d_parameters::print(), focus3d_parameters::set_default() and focus3d_parameters::test() apart from the overloaded assignment operator and the comparison operators. Note that the usage of assignment operator does not result in a shared memory.focus3d class
Objects of this class can be used to calculate the three-dimensional three-component focal fields. Instantiation of an object ( focus3d::focus3d() ) of this class is done by passing a focus3d_parameters object. Important methods which may be called before the actual calculation of the focal fields are focus3d::reset_parameters() to change the previously loaded parameters, focus3d::set_incident_field() to set the incident field, and focus3d::set_angular_weights to include the effects of scattering on the focal properties. Use focus3d::calculate_focus() method (either of the two variants) to perform this calculation. To save the results to the hard drive, use focus3d::save_results().dipole_radiation class
Objects of this class are used to calculate the far-field radiation from a distribution of dipoles near the focus of a collecting lens. Instantiation of an object ( dipole_radiation::dipole_radiation() ) of this class is done by passing a focus3d_paramters object. Important methods which may be called before the actual calculation of the far-field radiation are dipole_radiation::reset_parameters() to change the previously loaded parameters, and dipole_radiation::set_dipole_field() to set the distribution of radiating dipoles. To calculate the far-field radiation use dipole_radiation::calculate_radiation(). Often it is required to calculate the refracted radiation after the collecting lens. This is done by calling dipole_radiation::calculate_refraction() after invoking dipole_radiation::calculate_radiation() or directly using dipole_radiation::calculate_refracted_radiation(). Save the calculated results using dipole_radiation::save_results().Example Code
The package consists of, apert from the source files and the header files, a static library, libfocalfields.a in the lib/ directory of the package. Programmer should link this file while creating the executable. In the source code, only one header file namely, focalfields.h present in the include/ directory, needs to be included. For easy compilation, a makefile would be very helpful. Suppose mysource.cpp is the source tthat needs to be compiled to create an excutable, the following makefile can be used: LIBDIR = <focal-fields package dir>/lib/
INCLUDES = <focal-fields package dir>/include/
mysource.exe : mysource.cpp
g++ mysource.cpp -Wall -I$(INCLUDES) -L$(LIBDIR) -lm -lblitz -lfocalfields -o mysource.exe
Below is a listing of some of the example programs written using the focal fields package. They provide a good review of the essential commands required for efficiently using this package.
To calculate the focal field:
focal_volume.h#ifndef __FOCAL_VOLUME_H__ #define __FOCAL_VOLUME_H__ #include "focalfields.h" #endif
#include "focal_volume.h" int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc < 3) { cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <parameters file> <output directory>\n"; exit(-1); } string param_file = argv[1]; string outputdir = argv[2]; focus3d_parameters p; if(!p.load(param_file)) {exit (-1);} // load the parameters file p.print(); Array<complex<double>,3> E_focus1_x, E_focus1_y, E_focus1_z; Array<complex<double>,2> E_inc_x, E_inc_y, E_inc_z; E_focus1_x.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus1_x = 0; E_focus1_y.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus1_y = 0; E_focus1_z.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus1_z = 0; E_inc_x.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_inc_y.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_inc_z.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_inc_x = 1.0; E_inc_y = 0.0; E_inc_z = 0.0; focus3d focus1(p); focus1.set_incident_field(E_inc_x,E_inc_y,E_inc_z); focus1.calculate_focus(E_focus1_x,E_focus1_y,E_focus1_z); focus1.save_results(outputdir); return(0); }
To calculate the radiation from the focal volume:
radiation_from_focal_volume.h#ifndef __RADIATION_FROM_FOCAL_VOLUME_H__ #define __RADIATION_FROM_FOCAL_VOLUME_H__ #include "focalfields.h" #endif
#include "radiation_from_focal_volume.h" int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc < 3) { cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <parameters file> <output directory>\n"; exit(-1); } string param_file = argv[1]; string outputdir = argv[2]; focus3d_parameters p; if(!p.load(param_file)) {exit (-1);} // load the parameters file Array<complex<double>,2> E_rad_x, E_rad_y, E_rad_z; E_rad_x.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_rad_y.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_rad_z.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_rad_x = 0.0; E_rad_y = 0.0; E_rad_z = 0.0; dipole_radiation drad(p); drad.set_dipole_field("successive/focus1_lambda_0.8/E_focus_x.bar", \ "successive/focus1_lambda_0.8/E_focus_y.bar", \ "successive/focus1_lambda_0.8/E_focus_z.bar"); drad.calculate_refracted_radiation(E_rad_x,E_rad_y,E_rad_z); drad.save_results(outputdir); return(0); }
To calculate successive focus, radiation and focus:
successive_focus_radiate_focus.h#ifndef __SUCCESSIVE_FOCUS_RADIATE_FOCUS_H__ #define __SUCCESSIVE_FOCUS_RADIATE_FOCUS_H__ #include "focalfields.h" #endif
#include "successive_focus_radiate_focus.h" int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc < 3) { cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <parameters file> <output directory>\n"; exit(-1); } string param_file = argv[1]; string outputdir = argv[2]; focus3d_parameters p; if(!p.load(param_file)) {exit (-1);} // load the parameters file Array<complex<double>,2> E_inc_x, E_inc_y, E_inc_z; Array<complex<double>,3> E_focus1_x, E_focus1_y, E_focus1_z; Array<complex<double>,2> E_rad_x, E_rad_y, E_rad_z; Array<complex<double>,3> E_focus2_x, E_focus2_y, E_focus2_z; E_inc_x.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_inc_y.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_inc_z.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_inc_x = 1.0; E_inc_y = 0.0; E_inc_z = 0.0; E_focus1_x.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus1_x = 0; E_focus1_y.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus1_y = 0; E_focus1_z.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus1_z = 0; E_rad_x.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_rad_x = 0; E_rad_y.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_rad_y = 0; E_rad_z.resize(p.Ntheta,p.Nphi); E_rad_z = 0; E_focus2_x.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus2_x = 0; E_focus2_y.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus2_y = 0; E_focus2_z.resize(p.Nx,p.Ny,p.Nz); E_focus2_z = 0; cout << "---------------------------------------------\n"; cout << "---------------- first focus ----------------\n"; cout << "---------------------------------------------\n"; focus3d focus1(p); focus1.set_incident_field(E_inc_x,E_inc_y,E_inc_z); focus1.calculate_focus(E_focus1_x,E_focus1_y,E_focus1_z); focus1.save_results(string(outputdir + "/coarse_focus1")); cout << "---------------------------------------------\n"; cout << "------------------ radiation ----------------\n"; cout << "---------------------------------------------\n"; dipole_radiation drad(p); drad.set_dipole_field(E_focus1_x,E_focus1_y,E_focus1_z); drad.calculate_refracted_radiation(E_rad_x,E_rad_y,E_rad_z); drad.save_results(string(outputdir + "/coarse_radiation")); cout << "---------------------------------------------\n"; cout << "---------------- second focus ---------------\n"; cout << "---------------------------------------------\n"; focus3d focus2(p); focus2.set_incident_field(E_rad_x,E_rad_y,E_rad_z); focus2.calculate_focus(E_focus2_x,E_focus2_y,E_focus2_z); focus2.save_results(string(outputdir+"/coarse_focus2")); return(0); }
To calculate CARS excitation:
cars_excitation.h#ifndef __CARS_EXCITATION_H__ #define __CARS_EXCITATION_H__ #include "focalfields.h" #endif
#include "cars_excitation.h" int main(int argc, char** argv) { if(argc < 4) { cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " <pump-parameters file> <stokes-parameters file> <output directory>\n"; exit(-1); } string param_file_p = argv[1]; string param_file_s = argv[2]; string outputdir = argv[3]; stringstream filename; focus3d_parameters pp, ps, pc, temp; if(!pp.load(param_file_p)) {exit (-1);} // load the parameters file if(!ps.load(param_file_s)) {exit (-1);} // load the parameters file cout << "PUMP PARAMETERS:\n"; pp.print(); cout << "STOKES PARAMETERS:\n"; ps.print(); temp = pp; temp.lambda = ps.lambda; if(temp != ps) { cerr << "Input error! The spatial parameters in the two files do not match! Exiting\n"; exit(-1); } pc = ps; pc.lambda = 1.0/((2.0/pp.lambda) - (1.0/ps.lambda)); cout << "CARS PARAMETERS:\n"; pc.print(); Array<complex<double>,3> E_focus_pump_x, E_focus_pump_y, E_focus_pump_z; Array<complex<double>,3> E_focus_stokes_x, E_focus_stokes_y, E_focus_stokes_z; Array<complex<double>,3> cars_pol_x, cars_pol_y, cars_pol_z; Array<complex<double>,2> E_inc_x, E_inc_y, E_inc_z; E_focus_pump_x.resize(pp.Nx,pp.Ny,pp.Nz); E_focus_pump_x = 0; E_focus_pump_y.resize(pp.Nx,pp.Ny,pp.Nz); E_focus_pump_y = 0; E_focus_pump_z.resize(pp.Nx,pp.Ny,pp.Nz); E_focus_pump_z = 0; E_focus_stokes_x.resize(ps.Nx,ps.Ny,ps.Nz); E_focus_stokes_x = 0; E_focus_stokes_y.resize(ps.Nx,ps.Ny,ps.Nz); E_focus_stokes_y = 0; E_focus_stokes_z.resize(ps.Nx,ps.Ny,ps.Nz); E_focus_stokes_z = 0; cars_pol_x.resize(ps.Nx,ps.Ny,ps.Nz); cars_pol_x = 0; cars_pol_y.resize(ps.Nx,ps.Ny,ps.Nz); cars_pol_y = 0; cars_pol_z.resize(ps.Nx,ps.Ny,ps.Nz); cars_pol_z = 0; E_inc_x.resize(pp.Ntheta,pp.Nphi); E_inc_y.resize(pp.Ntheta,pp.Nphi); E_inc_z.resize(pp.Ntheta,pp.Nphi); E_inc_x = 1.0; E_inc_y = 0.0; E_inc_z = 0.0; cout << "Calculating pump focal field\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"; focus3d focus_pump(pp); focus_pump.set_incident_field(E_inc_x,E_inc_y,E_inc_z); focus_pump.calculate_focus(E_focus_pump_x,E_focus_pump_y,E_focus_pump_z); focus_pump.save_results(outputdir+"pump"); E_inc_x.resize(ps.Ntheta,ps.Nphi); E_inc_y.resize(ps.Ntheta,ps.Nphi); E_inc_z.resize(ps.Ntheta,ps.Nphi); E_inc_x = 1.0; E_inc_y = 0.0; E_inc_z = 0.0; cout << "Calculating stokes focal field\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"; focus3d focus_stokes(ps); focus_stokes.set_incident_field(E_inc_x,E_inc_y,E_inc_z); focus_stokes.calculate_focus(E_focus_stokes_x,E_focus_stokes_y,E_focus_stokes_z); focus_stokes.save_results(outputdir+"stokes"); complex<double> chi = 2.0; cout << "Calculating CARS excitation\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"; cars_pol_x = chi*E_focus_pump_x*E_focus_pump_x*conj(E_focus_stokes_x); cars_pol_y = chi*E_focus_pump_y*E_focus_pump_y*conj(E_focus_stokes_y); cars_pol_z = chi*E_focus_pump_z*E_focus_pump_z*conj(E_focus_stokes_z); cout << "Saving CARS excitation\n~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~\n"; ofstream fout; filename.str(string()); filename << outputdir << "cars_excitation_x.bar"; cout << filename.str() << endl; fout.open(filename.str().c_str()); if(!fout) { cerr << "File error!! Unable to write " << filename.str() << endl; exit(-1); } fout << cars_pol_x; fout.close(); filename.str(string()); filename << outputdir << "cars_excitation_y.bar"; cout << filename.str() << endl; fout.open(filename.str().c_str()); if(!fout) { cerr << "File error!! Unable to write " << filename.str() << endl; exit(-1); } fout << cars_pol_y; fout.close(); filename.str(string()); filename << outputdir << "cars_excitation_z.bar"; cout << filename.str() << endl; fout.open(filename.str().c_str()); if(!fout) { cerr << "File error!! Unable to write " << filename.str() << endl; exit(-1); } fout << cars_pol_z; fout.close(); filename.str(string()); filename << outputdir << "cars_simulation_parameters.dat"; cout << filename.str() << endl; pc.save(filename.str()); return(0); }
 1.5.5
1.5.5